Are you tired of dealing with chronic inflammation and its negative effects on your health?
While there are many diets out there claiming to reduce inflammation, you may be skeptical about the effectiveness of the ketogenic diet. However, before you dismiss it completely, consider this: the ketogenic diet has been gaining popularity as a powerful tool in reducing inflammation and improving overall health.
But how does it work? In this guide, we will explore the science behind the ketogenic diet and provide you with practical tips on how to incorporate it into your lifestyle.
So, if you're ready to discover a natural way to combat inflammation, keep reading to uncover the secrets of the ketogenic diet.
Understanding Inflammation and Its Effects
Understanding inflammation and its effects is crucial for anyone looking to improve their health and well-being. Inflammatory diseases, such as arthritis, asthma, and autoimmune disorders, can have a significant impact on daily life. Inflammation is the body's natural response to injury or infection, but when it becomes chronic, it can lead to long-term health problems. Chronic inflammation has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Fortunately, there are natural remedies that can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health. One such remedy is adopting a ketogenic diet. The ketogenic diet is a low-carb, high-fat diet that has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects. By restricting carbohydrates and increasing healthy fats, the ketogenic diet can help regulate the body's inflammatory processes.
Research has shown that the ketogenic diet can decrease levels of inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein and interleukin-6. It can also reduce oxidative stress, which is a major contributor to chronic inflammation. Additionally, the diet promotes weight loss, which can further reduce inflammation in the body.
Incorporating natural anti-inflammatory foods into your ketogenic diet can also provide additional benefits. Foods such as fatty fish, olive oil, nuts, and leafy greens are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, which have been shown to reduce inflammation.
Understanding inflammation and its effects is the first step towards improving your health. By adopting a ketogenic diet and incorporating natural remedies, you can reduce inflammation and promote overall well-being.
The Basics of the Ketogenic Diet
To successfully implement the ketogenic diet and reap its anti-inflammatory benefits, it's essential to understand the basics of this low-carb, high-fat eating plan. The ketogenic diet is designed to shift your body into a state of ketosis, where it primarily burns fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. This metabolic state has been shown to have numerous health benefits, including reducing inflammation.
To understand the basics of the ketogenic diet, it's important to familiarize yourself with the concept of macros. Macros, short for macronutrients, are the three main nutrients your body needs for energy: carbohydrates, protein, and fat. The ketogenic diet focuses on drastically reducing your carbohydrate intake and increasing your fat intake, while maintaining a moderate protein intake.
Here are the key points to understand about the ketogenic diet:
- Low carbohydrate intake: The main principle of the ketogenic diet is to restrict your carbohydrate intake to a very low level, typically around 20-50 grams per day.
- High fat intake: To compensate for the reduced carbohydrates, you'll consume a higher amount of healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
- Moderate protein intake: While protein is an important part of the diet, consuming too much can hinder ketosis. It's essential to strike a balance and consume a moderate amount of protein.
The benefits of ketosis, the metabolic state achieved through the ketogenic diet, include reduced inflammation. By understanding the basics of the ketogenic diet and implementing it correctly, you can harness its anti-inflammatory properties and promote overall health and well-being.
How the Ketogenic Diet Reduces Inflammation

The ketogenic diet has been shown to effectively reduce inflammation through the process of ketosis. When you follow a ketogenic diet, your body enters a state of ketosis, where it burns fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. This shift in fuel source has several benefits for reducing inflammation.
Firstly, the ketogenic diet helps to stabilize blood sugar levels. By avoiding high-carbohydrate foods, you prevent spikes in blood sugar and insulin levels, which can contribute to chronic inflammation.
Additionally, ketones, the byproducts of fat metabolism, have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties. They can help reduce the production of pro-inflammatory molecules in the body, thus reducing inflammation.
Furthermore, the ketogenic diet promotes weight loss, which can also help to reduce inflammation. Excess body fat is associated with increased levels of inflammation in the body. By following a ketogenic diet and losing weight, you can decrease the burden on your body and reduce inflammation.
Getting Started With the Ketogenic Diet
After learning about how the ketogenic diet reduces inflammation, it's important to know how to get started with this beneficial eating plan. Here are some practical steps to help you begin:
- Research and Educate Yourself: Take the time to learn about the ketogenic diet and its principles. Understand how it can reduce inflammation and improve your overall health.
- Meal Prepping: Plan and prepare your meals in advance. This will help you stick to the diet and ensure you have nutritious options readily available. Focus on incorporating low-carb, high-fat foods like avocados, nuts, and fatty fish into your meals.
- Tracking Macros: Keep track of your macronutrient intake, specifically your carbohydrate, fat, and protein consumption. This will help you ensure you're staying within the recommended ranges for the ketogenic diet.
- Gradual Transition: Rather than making abrupt changes, gradually reduce your carbohydrate intake while increasing your fat intake. This will help your body adjust to using fat as its primary fuel source.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and support your body's functions during the transition to ketosis.
Choosing the Right Foods for a Ketogenic Diet

When following a ketogenic diet, it's important to choose the right foods that are low in carbohydrates and high in healthy fats. This will help your body enter a state of ketosis, where it burns fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates.
To make it easier to stick to your ketogenic diet, consider meal prepping. This involves planning and preparing your meals in advance, so you always have keto-friendly options on hand.
When it comes to choosing the right foods, focus on whole, unprocessed options. Include plenty of low-carb vegetables like leafy greens, broccoli, and cauliflower. These provide important vitamins and minerals while keeping your carbohydrate intake in check. Incorporate healthy fats such as avocados, olive oil, and nuts into your meals. These fats not only help you reach your daily fat intake but also provide anti-inflammatory benefits.
To add variety to your meals, explore ketogenic recipes. There are numerous resources available online that offer delicious and creative ideas for keto-friendly meals. From cauliflower pizza crusts to zucchini noodles, the options are endless. Experiment with different flavors and ingredients to keep your meals interesting and enjoyable.
Remember to read labels and choose ingredients that align with your ketogenic goals.
Meal Planning for a Ketogenic Diet
To effectively plan your meals for a ketogenic diet, you can take advantage of meal prepping techniques that align with your low-carb, high-fat goals. Meal prepping allows you to save time and ensure you have keto-friendly options readily available.
Here are some tips to help you with your meal planning for a ketogenic diet:
- Plan your meals in advance: Dedicate some time each week to plan out your meals and snacks. This will help you stay on track and avoid reaching for carb-heavy options when you're hungry and unprepared.
- Focus on macros: Tracking macros, which are the macronutrients – fat, protein, and carbohydrates – in your meals, is essential for a successful ketogenic diet. Use a food tracking app to ensure you're getting the right balance of these nutrients.
- Batch cook: Prepare large batches of keto-friendly recipes, such as casseroles or stews, that can be divided into individual portions and stored in the fridge or freezer. This way, you'll always have a quick and easy keto meal on hand.
- Use versatile ingredients: Choose ingredients that can be used in multiple dishes, such as eggs, avocados, and cauliflower. This will help you save money and reduce waste.
- Keep it simple: Don't feel the need to make elaborate meals every day. Stick to simple recipes that are easy to prepare and require minimal ingredients.
Incorporating Healthy Fats Into Your Diet
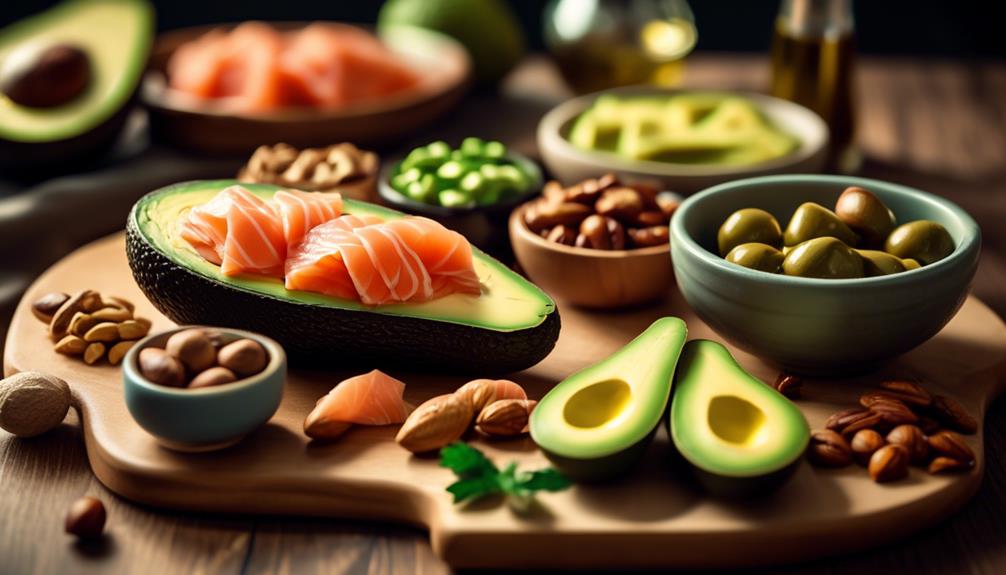

To incorporate healthy fats into your ketogenic diet, focus on consuming foods rich in essential omega-3 fatty acids such as fatty fish, chia seeds, and flaxseeds. These fats have been shown to reduce inflammation and support overall health.
Additionally, consider incorporating nourishing sources of fat like avocado and olive oil, which are packed with monounsaturated fats that can help reduce inflammation and promote heart health.
Coconut oil is another great option as it contains medium-chain triglycerides that can provide quick energy and support ketosis.
Essential Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Incorporate essential omega-3 fatty acids into your diet to promote a healthy balance of fats and reduce inflammation. Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA found in fish oil, have been shown to offer numerous health benefits. Here are some key reasons why you should consider adding omega-3 fatty acids to your daily routine:
- Omega-3 supplements: Taking omega-3 supplements can help ensure you're getting an adequate amount of these essential fats, especially if you don't consume fish regularly.
- Fish oil benefits: Research suggests that fish oil can help reduce inflammation, decrease triglyceride levels, improve brain health, and support heart health.
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that can help alleviate symptoms of chronic inflammation, such as joint pain and swelling.
- Heart health: Studies have shown that omega-3 fatty acids can reduce the risk of heart disease by lowering blood pressure and improving cholesterol levels.
Nourishing Avocado and Olive Oil
Incorporating nourishing avocado and olive oil into your diet is a simple and effective way to incorporate healthy fats and continue promoting a balanced intake of fats while reducing inflammation.
Avocado oil is rich in monounsaturated fats, which have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties. This makes it a great choice for cooking and dressing salads. You can also use avocado oil in baking and as a replacement for butter or margarine.
Olive oil, on the other hand, is known for its high content of oleic acid, a monounsaturated fat that has been linked to reduced inflammation and improved heart health. It's a versatile oil that can be used for cooking, drizzling on salads, or as a dip for bread.
To incorporate avocado and olive oil into your diet, try making avocado oil-based dressings or using olive oil in your favorite recipes. The benefits of these healthy fats extend beyond reducing inflammation, so make sure to incorporate them into your overall dietary plan.
Coconut Oil Benefits
Including coconut oil in your diet can provide numerous benefits and contribute to a healthy intake of fats. Coconut oil is rich in medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which have been shown to promote weight loss and improve brain function.
Here are some key benefits of incorporating coconut oil into your diet:
- Boosts metabolism: MCTs in coconut oil can increase calorie burning and boost your metabolic rate.
- Supports heart health: Coconut oil is high in lauric acid, which has been linked to improved cholesterol levels and reduced risk of heart disease.
- Enhances skin health: Coconut oil can be used topically as a moisturizer, helping to hydrate and nourish your skin.
- Provides energy: MCTs are easily absorbed by the body and quickly converted into energy, making coconut oil a great source of fuel for physical activity.
To incorporate coconut oil into your diet, you can try using it in cooking, baking, or even adding it to your coffee or smoothies. For skincare, you can use coconut oil as a natural moisturizer or create homemade beauty products using coconut oil recipes.
Limiting Carbohydrates on a Ketogenic Diet

When it comes to reducing inflammation, limiting carbohydrates is a key aspect of a ketogenic diet. By restricting carb intake, your body enters a state of ketosis, where it burns fat for fuel instead of relying on glucose from carbs.
This shift in metabolism has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects and can help reduce chronic inflammation associated with various health conditions.
Carb Restriction for Inflammation
To effectively reduce inflammation on a ketogenic diet, it's crucial to limit the intake of carbohydrates. Carb restriction offers several benefits in terms of inflammation reduction. By reducing carbohydrates, you lower your blood sugar levels, which in turn helps to reduce the production of pro-inflammatory molecules. Additionally, limiting carbs promotes weight loss, which has been shown to decrease inflammation in the body.
However, carb restriction also comes with its challenges. It can be difficult to adjust to a low-carb diet, as many commonly consumed foods are high in carbohydrates. It may also lead to initial side effects such as fatigue and irritability, known as the 'keto flu.'
Nevertheless, with proper planning and education, these challenges can be overcome, making carb restriction a valuable tool in reducing inflammation on a ketogenic diet.
Ketosis and Inflammation
Limiting carbohydrates on a ketogenic diet is a key strategy for achieving and maintaining a state of ketosis, which can help reduce inflammation in the body. Ketosis is a metabolic state in which the body produces ketones from fat as its primary source of fuel instead of glucose from carbohydrates.
This shift in fuel utilization has been shown to have several benefits for inflammation. Firstly, ketones have been found to have anti-inflammatory properties, reducing the levels of pro-inflammatory molecules in the body. Additionally, the ketogenic diet has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, which can help reduce chronic inflammation.
However, it's important to note that entering ketosis can also have some risks, such as the potential for nutrient deficiencies and an increased risk of kidney stones. It's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting a ketogenic diet to ensure it's safe and appropriate for your individual needs.
Benefits of Low-Carb Diet
One effective strategy for reducing inflammation is by limiting carbohydrates on a ketogenic diet. By following a low-carb diet, you can experience several benefits that contribute to your overall health and well-being.
Here are some key advantages of incorporating a low-carb diet into your lifestyle:
- Weight Loss:
A low-carb diet can lead to significant weight loss due to reduced calorie intake and improved fat burning. It promotes the consumption of nutrient-dense foods that keep you feeling satisfied and prevent overeating.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity:
Restricting carbohydrates can enhance insulin sensitivity, which helps regulate blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. It promotes better utilization of glucose and prevents insulin resistance, a common precursor to chronic inflammation.
Monitoring Protein Intake on a Ketogenic Diet
Monitoring your protein intake is an essential aspect when following a ketogenic diet, as it helps ensure you stay within the appropriate range to maintain ketosis and effectively reduce inflammation. Protein tracking is crucial because consuming too much protein can kick you out of ketosis, while consuming too little can lead to muscle loss and inadequate nutrition.
To monitor your protein intake, you can use various tools and methods. One effective way is to track your macros using a food diary or a mobile app. These tools allow you to input the foods you eat and calculate the amount of protein you consume. Aim to consume around 0.6-1 gram of protein per pound of lean body mass to maintain muscle mass and support bodily functions.
Additionally, measuring inflammation markers can help you gauge the effectiveness of your protein intake. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) are commonly used to assess inflammation levels. Regularly monitoring these markers can provide insights into how your protein intake is impacting inflammation in your body.
Adding Anti-Inflammatory Spices and Herbs to Your Meals
Spice up your meals and boost your health by adding anti-inflammatory spices and herbs.
These flavorful inflammation fighters not only add a burst of flavor to your dishes but also provide numerous health benefits.
Incorporating spices like turmeric, ginger, cinnamon, and herbs like rosemary and basil can help reduce inflammation and promote overall well-being.
Flavorful Inflammation Fighters
Enhance the anti-inflammatory power of your meals by incorporating a variety of flavorful spices and herbs. Adding these inflammation-fighting ingredients to your dishes not only enhances the taste but also provides numerous health benefits.
Here are some ideas on how to incorporate spices and herbs into your meals:
- Turmeric: Known for its powerful anti-inflammatory properties, turmeric contains a compound called curcumin. Add a pinch of turmeric to your dishes or enjoy a warm cup of turmeric tea.
- Ginger: Ginger has been used for centuries to reduce inflammation. Grate fresh ginger into stir-fries or add it to your morning smoothie for an extra kick.
- Cayenne pepper: This fiery spice contains capsaicin, which has been shown to reduce inflammation. Sprinkle cayenne pepper on roasted vegetables or add it to homemade spice blends.
Spice up Your Health
To further optimize the anti-inflammatory benefits of your meals, consider incorporating a variety of flavorful spices and herbs into your cooking routine. Not only do spices and herbs add depth and complexity to your dishes, but they also offer numerous health benefits.
When it comes to anti-inflammatory properties, turmeric is a standout. Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, has been shown to reduce inflammation in the body. You can easily incorporate turmeric into your meals by adding it to curries, soups, or even smoothies.
Other anti-inflammatory spices and herbs include ginger, garlic, cinnamon, and rosemary. Experiment with different combinations to find your favorite anti-inflammatory recipes.
Hydration and Its Role in Reducing Inflammation

Staying properly hydrated is crucial for reducing inflammation and maintaining overall health. Adequate hydration helps to ensure that your body functions optimally, including the proper functioning of your immune system, which plays a key role in controlling inflammation.
Here are two important factors to consider regarding hydration and its role in reducing inflammation:
Importance of hydration:
- Water is essential for all bodily functions, including the transport of nutrients and oxygen, the regulation of body temperature, and the elimination of waste products.
- Proper hydration helps to keep your joints lubricated and reduces the risk of joint inflammation and pain.
Role of electrolytes:
- Electrolytes are minerals that help regulate the balance of fluids in your body. They include sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium.
- Electrolytes play a crucial role in maintaining proper fluid balance, nerve function, muscle contraction, and regulating pH levels.
To ensure adequate hydration, drink water throughout the day, especially during periods of physical activity or when exposed to hot weather. Additionally, consuming foods rich in electrolytes, such as fruits, vegetables, and electrolyte-enhanced beverages, can help maintain the balance of fluids in your body.
Remember to listen to your body's thirst cues and aim for clear or pale yellow urine as a sign of proper hydration. By prioritizing hydration and electrolyte balance, you can support your body in reducing inflammation and promoting overall health.
Incorporating Intermittent Fasting With the Ketogenic Diet
If you're looking to maximize the benefits of the ketogenic diet for reducing inflammation, incorporating intermittent fasting can be a valuable strategy.
Fasting has been shown to promote autophagy, a process that helps remove damaged cells and reduce inflammation in the body.
Benefits of Fasting
- Reduced oxidative stress: Intermittent fasting and the ketogenic diet can reduce oxidative stress in the body, which is a major contributor to inflammation and chronic diseases.
- Improved brain function: Fasting and the ketogenic diet have been shown to enhance brain function and protect against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's.
- Increased energy levels: By promoting fat burning and stabilizing blood sugar levels, intermittent fasting and the ketogenic diet can increase energy levels throughout the day.
- Balanced hormones: Fasting and the ketogenic diet can help balance hormones in the body, which is important for reducing inflammation and promoting overall health.
- Improved digestion: Intermittent fasting can give the digestive system a break, allowing it to heal and function more efficiently, reducing inflammation in the gut.
- Enhanced longevity: Studies have shown that intermittent fasting and the ketogenic diet can extend lifespan and promote healthy aging by reducing inflammation and improving overall health.
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases: Incorporating intermittent fasting with the ketogenic diet has been shown to reduce the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and cancer, which are all linked to inflammation.
Timing Your Meals
To effectively incorporate intermittent fasting with the ketogenic diet, consider timing your meals strategically for optimal results in reducing inflammation and promoting overall health.
Meal timing plays a crucial role in how your body responds to food and influences various metabolic processes. Intermittent fasting involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting, which can help enhance the benefits of the ketogenic diet.
One popular approach is the 16/8 method, where you fast for 16 hours and limit your eating window to 8 hours each day. This allows your body to enter a state of ketosis and utilize stored fat for energy.
By aligning your meals with the fasting period, you can maximize the anti-inflammatory effects of ketones and promote cellular repair and regeneration. Experiment with different meal timing strategies to find what works best for you and your lifestyle.
Remember to prioritize nutrient-dense, keto-friendly foods during your eating window to support your overall health and well-being.
Tips for Sticking to a Ketogenic Diet Long-Term

To maintain a ketogenic diet long-term, it's important to implement strategies that support consistency and adherence. Here are some tips to help you stick to your keto lifestyle:
- Tips for Meal Prep:
- Plan your meals in advance: Take some time each week to plan your meals and snacks. This will help you stay on track and avoid making impulsive food choices.
- Cook in batches: Prepare larger portions of keto-friendly meals and store them in individual containers. This will save you time and ensure you always have a healthy option ready to eat.
- Finding Keto-Friendly Snacks:
- Stock up on low-carb snacks: Keep your pantry and fridge filled with keto-friendly snacks, such as nuts, seeds, cheese, and jerky. These will help you curb cravings and stay satisfied between meals.
- Explore keto recipes: Look for recipes that recreate your favorite snacks with keto-friendly ingredients. For example, you can make your own kale chips or cheese crisps as a crunchy alternative to carb-heavy snacks.
Monitoring and Evaluating Your Progress
Regularly track and assess your progress to ensure you're effectively following the ketogenic diet and achieving your health goals. Monitoring and evaluating your progress is crucial for staying on track and making necessary adjustments.
There are several ways you can track your progress and measure the effectiveness of the ketogenic diet.
One method is to keep a food diary. This allows you to record everything you eat and drink, making it easier to identify any deviations from the diet. It also helps you track your macronutrient intake to ensure you're meeting the recommended ratios of fat, protein, and carbohydrates.
Another way to evaluate your progress is by tracking your weight and body measurements. Keep a record of your weight, waist circumference, and other relevant measurements. This will give you a clear picture of any changes in your body composition.
In addition, consider tracking other health markers such as blood glucose levels, cholesterol levels, and inflammation markers. These can provide valuable insights into how the ketogenic diet is affecting your overall health.
Lastly, don't forget to track how you feel. Pay attention to your energy levels, mood, and any improvements in symptoms related to inflammation. These subjective measures can be just as important as objective measurements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the ketogenic diet offers a practical and evidence-based approach to reducing inflammation in the body. By understanding the basics of the diet and choosing the right foods, individuals can experience the benefits of decreased inflammation.
Hydration and intermittent fasting can also play a role in supporting this process. By following these tips and monitoring progress, individuals can enjoy the long-term benefits of a ketogenic lifestyle.







